One measure of
software quality is the number of coding errors made by programmers by 1000
lines of code (KLOC = a thousand lines of code). The probability that a
programmer will make no errors is 0.05, from 1 to 3 errors per KLOC is 0.65,
and the probability of making anywhere from 4 to 6 errors per KLOC is 0.20. The
probability of that the programmer will make at least 4 errors is
0.20
0.85
0.90
0.30
When we sample
from an infinite population, what happens to the standard error of the mean
when the sample size is decreased from 1000 to 10.
It is reduced and is 10 times smaller.
It stays the same.
It is increased and is 10 times larger.
It is increased and is 100 times larger.
A researcher
wants to select a stratified sample of size 40 from a population of size
N = 1,000, which consists of four strata of size
N1 = 250,
N2 = 600, N3 = 100 and N4 = 50. If the research wants to
obtain a proportional allocation, how large the sample should be from each
stratum?
12, 18, 7, 3
10, 18, 8, 4
10, 24, 4, 2
10, 10, 10, 10
In a certain
experiment, a null hypothesis is rejected at the 0.05 level of significance.
This means that
The probability that the null hypothesis is true is at most 0.05.
The probability that the alternative hypothesis is false is at most 0.05.
The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true is at most 0.05.
The probability that the alternative hypothesis is true is at most 0.05.
A substantial
part of the U.S. population is "technologically illiterate" according to
experts at a National Technological Literacy Conference organized by the
National Science foundation and Pennsylvania State University At this
conference, the results of a national survey of 2,000 adults showed that 75% do
not have a clear understanding on what computer software is. A new survey found
that 267 out of 400 individuals do not have a clear understanding of computer
software. Does this new survey show that adults have become more
technologically literate? Compute a statistical test for the hypotheses Ho: p =
0.75 vs Ha: p<0.75, where p = "true proportion of adults that do not have a
clear understanding of computer software." What is the distribution of the test
statistic?
Approximately N(0.75, 0.0217)
Approximately N(0.6675, 0.0217)
Approximately N(0.6675, 0.0236)
Approximately N(0.75, 0.0236)
Suppose that
number of times that a software company's customer service representative take
to respond to trouble calls is normally distributed with mean ÎĽ and standard
deviation Ďƒ = 0.23 hours. The company advertises that its customer service
take an average of no more than 2 hours to respond to trouble calls from
customers.
From a random sample of 25 trouble calls, the average time service technicians
took to respond was 2.10 hours. To investigate the company claim, the
following test is computed: null hypothesis Ho: ÎĽ <= 2h and alternative
hypothesis Ha: ÎĽ > 2 h. The 95% C.I. for the average time of response
to a call is (2.054h, 2.146h).
H0 can be rejected at 1%
significance level because 2h is not within confidence interval.
H0
can be rejected at 5% level
significance, but this must be determined by carrying out the hypothesis test
rather than using the confidence interval.
We can be
certain that H0 is not true.
H0
can be rejected at 5%
significance level because 2h is within confidence interval.
You are
thinking of using a t -procedure to compute a statistical test on
population averages. You suspect the distribution of the population is not
normal and may be skewed. Which of the following statements is correct?
You should not use the t-procedure since the population
does not have a normal distribution.
You may use the t-procedure provided your sample size is large,
say at least 50.
You may use the t-procedure since it is robust to nonnormality.
Data were collected
on X = yearly income (in thousands of dollars per year) of home purchasers and
Y = sale price of the house (in thousands of dollars). The income of the purchaser
varied between 40,000 dollars and 70,000 dollars. The table below shows the results
of the regression analysis to fit the regression line of house sale price
versus yearly income.
|
Price
|
Coeff
|
Std.
Error
|
t
|
P>|t|
|
|
Income
|
2.461967
|
0.108803
|
22.628
|
0.000
|
|
Intercept
|
24.35755
|
4.286011
|
5.683
|
0.000
|
Compute the predicted sale price of a house purchased by a
person with 50,000 dollars yearly income, therefore, for x = 50.0 (in thousands
of dollars).
The predicted sale price is 147,460 dollars.
You cannot use
the regression line because the results in the table show that there is no
significant linear relationship between yearly income and house sale price.
The predicted sale price is 97,260 dollars.
You cannot compute the predicted value because there were no
purchasers in the sample
with income equal to 50,000 dollars.
Which of the
following is true of the slope of the least-squares regression line?
It has the same sign as the correlation coefficient.
The square of the slope equals the fraction of the variation
in the response variable that is explained by the explanatory variable.
It is unitless.
All of the above.
After
computing the least-squares regression line, you observed that the sample
contains an influential point. Which of the following statements is true?
Deleting the
influential point should reduce the correlation and improve the fit.
Deleting the
influential point will not significantly change the regression line.
Deleting
the influential point should increase the correlation and improve the fit.
None of the above.
The following
data descriptor is a resistant measure to outliers:
Mean
Median
Standard Deviation
Correlation
A normal density curve has which of the following properties?
It is symmetric.
It has a peak centered above its mean.
The spread of the curve is proportional to the standard deviation.
All of the above.
A pediatrician
obtains the heights of her 200 three-year-old female patients. The heights are
normally distributed, with mean 38.72 and standard deviation 3.17. The percent
of the three-year-old females have a height less than 35 inches is:
12.10
87.90
49%
51%
Below is a plot of the Olympic gold medal winning
performance in the high jump (in inches) for the years 1900 to 1996.
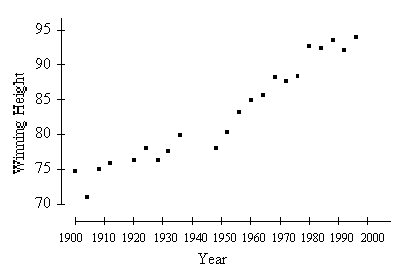
From this plot, the correlation between the winning height
and year of the jump is
about 0.95
about 0.10
about -0.50
about 0.50
A survey of 1000 adults ages
30 to 35 is conducted. The number of years of schooling and the annual salary
for each person in the survey is recorded. The correlation between years of schooling
and annual salary is found to be 0.27. Suppose instead, the average salary of
all individuals in the survey with the same number of years of schooling was
calculated and the correlation between these averages and years of schooling
was computed. This correlation would most likely be
equal to 0.27
greater than 0.27
less than 0.27
Other things being equal, the margin of error of a confidence interval
increases as
the sample size increases
the confidence level decreases
the population standard deviation increases
none of the above
Crop researchers plant 100
plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is equal to
130 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield per acre for the new variety of
corn follows a normal distribution with unknown mean ÎĽ and standard deviation
Ďƒ equal to 10 bushels per acre. A 90% confidence interval for ÎĽ is
130 ± 1.645
130 ± 1.96
130 ± 16.45
To assess the accuracy of a
kitchen scale a standard weight known to weigh 1 gram is weighed a total of n
times and the mean ÎĽ,
of the weightings is computed. Suppose the scale readings are normally
distributed with unknown mean, ÎĽ, and standard deviation
Ďƒ = 0.01 g. How large should n be
so that a 90% confidence interval for μ has a margin of error of ± 0.0001?
165
27065
38416
You
measure the heights of a random sample of 400 high school sophomore males in a
Midwestern state. The sample mean is 66.2. Suppose that the heights of the
population of all high school sophomore males follow a normal distribution with
unknown mean ÎĽ and standard deviation Ďƒ = 4.1 inches. A 95% confidence interval
for ÎĽ is:
(58.16, 74.24)
(59.46, 72.94)
(65.8, 66.6)
(65.86, 66.54)
A sample was taken of the salaries of four employees from a large company. The
following are their salaries (in thousands of dollars)
for this year:
33 31 24 26. The variance of their salaries is:
5.1
26
31